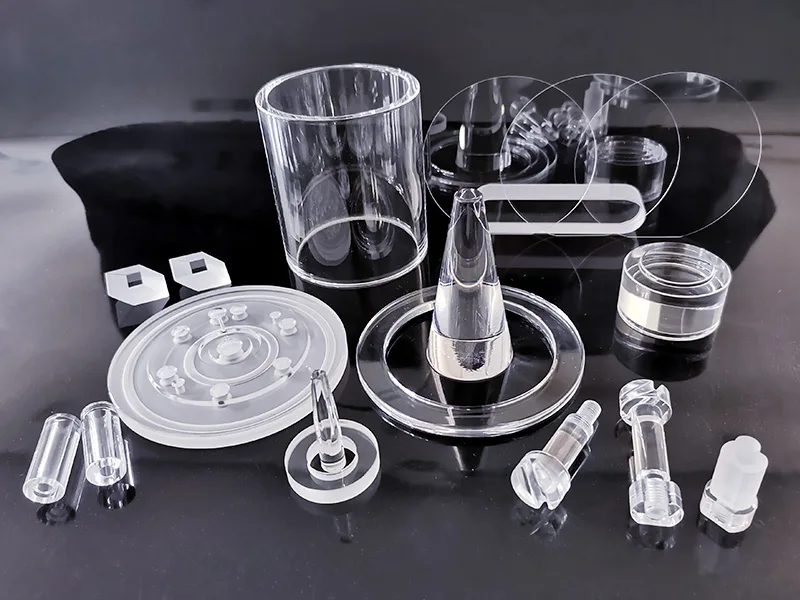
Introduction to Quartz Glass in Semiconductor Applications
Quartz glass, also known as fused quartz, is a critical material widely utilized in the semiconductor industry due to its exceptional properties and performance characteristics. Made from high purity silica, quartz glass achieves a purity level of 99.99% SiO2, making it highly suitable for various applications in semiconductor manufacturing. This remarkable level of purity reduces the likelihood of contamination, ensuring the cleanliness required for advanced production processes. In semiconductor fabrication, even minimal impurities can significantly affect wafer yield and overall device performance.
The inherent properties of quartz glass make it an ideal choice for critical semiconductor processes, such as photolithography, where the transmission of ultraviolet light through quartz tubes for diffusion furnaces is essential. The ability to withstand high temperatures and resist thermal shock further underscores the suitability of quartz in high-precision applications. Additionally, its low thermal expansion coefficient is crucial for maintaining dimensional stability during rapid temperature transitions, which is a common occurrence in semiconductor processing.
Another significant aspect of quartz glass is its role in contamination control quartzware. Maintaining a contamination-free environment is vital in semiconductor manufacturing, as even minute particles can result in defects and reduced yields. Consequently, using high purity fused quartz semiconductor components is fundamental for achieving optimal results in device fabrication.
As we delve deeper into the discussion of quartz glass purity, it becomes evident that the implications of purity levels cannot be overstated. The high purity achieved through stringent manufacturing processes ensures that impurities are minimized, providing a reliable foundation for semiconductor applications. In the subsequent sections, we will explore the effects of impurities on wafer yield, further highlighting the importance of quartz glass in the semiconductor industry.
What is Quartz Glass and its Composition?
Quartz glass, often referred to as fused quartz or silica glass, is a type of glass that is primarily composed of silicon dioxide (SiO2). With a composition of approximately 99.99% SiO2, quartz glass boasts a remarkable degree of purity which is essential in semiconductor manufacturing. This high purity ensures that the material’s physical and chemical properties are maximized, making it an ideal choice for a variety of semiconductor applications.
The formation of quartz glass occurs through the heating and melting of high purity silica, derived from natural sources such as sandstone, quartzite, and other silicate minerals. During the manufacturing process, the silica undergoes a melting process at high temperatures, often exceeding 1680°C. This results in a non-crystalline structure that enhances the optical clarity and mechanical strength of the glass. The purity of the starting materials directly contributes to the final product’s quality, influencing the performance of semiconductor grade quartz components in various applications.
As a cornerstone in the semiconductor industry, the characteristics of quartz glass play a vital role in fabrication processes. Purity levels in excess of 99.99% are critical in minimizing the effects of impurities on wafer yield during semiconductor production. The presence of contaminants can significantly impact the electrical properties of silicon wafers, leading to potential defects and failures. Hence, contamination control quartzware is preferred to ensure that the integrity of the manufacturing process remains intact.
In summary, quartz glass is formed primarily from SiO2 and distinguished by its high purity, making it essential for applications that require enhanced optical and electrical properties. Understanding its composition is fundamental for those involved in semiconductor manufacturing, as it directly relates to the performance and reliability of semiconductor devices.
The Importance of Purity Levels in Quartz Glass
In the realm of semiconductor manufacturing, the purity of materials used plays a pivotal role in determining the success and efficiency of the final products. High purity fused quartz semiconductor materials, particularly those with a quartz glass purity of 99.99% SiO2, are essential in optimizing performance and ensuring reliability in semiconductor devices. The presence of even minuscule amounts of impurities can have significant repercussions on various aspects of semiconductor performance, making contamination control quartzware critical.
Impurities in quartz glass can lead to several adverse effects, including decreased electrical performance and thermal stability. These impurities can originate during the manufacturing process or arise from environmental sources, thus necessitating stringent control measures. The effects of impurities on wafer yield are notable; if contaminants infiltrate the semiconductor fabrication process, they can result in defects and ultimately reduce the overall yield of productive wafers. Such challenges emphasize the crucial need for semiconductor grade quartz components that exhibit exceptional purity levels.
The integration of high purity fused quartz semiconductor materials is especially important in applications involving quartz tubes for diffusion furnaces. These tubes must maintain the integrity and purity of the materials being processed, as any contamination introduced can significantly alter the properties of the semiconductors produced. Therefore, manufacturers are increasingly prioritizing the use of high-purity quartz materials to uphold quality standards and improve device performance.
In conclusion, maintaining high purity levels in quartz glass is not merely a guideline but a necessity in semiconductor manufacturing. The reliance on materials like 99.99% SiO2 serves to enhance the performance, efficiency, and reliability of semiconductor devices, ultimately impacting the overarching success of the technology sector.
Defining 99.99% SiO2: What It Means for Quality
The specification of 99.99% SiO2 purity refers to the exceptionally high quality of silicon dioxide used in semiconductor manufacturing, particularly relevant for high purity fused quartz semiconductor applications. At this level, it is understood that the SiO2 material comprises 99.99% silicon dioxide, implying a mere 0.01% of impurities. This minute presence of contaminants can significantly impact the performance of semiconductor components, affecting factors such as wafer yield and overall device reliability.
To achieve 99.99% SiO2 purity, stringent standards are established and must be adhered to during the fabrication of quartz materials. These specifications encompass the source materials utilized, the manufacturing processes employed, and the conditions under which the quartzware is handled. Advanced methods such as high-temperature cleaning and rigorous contamination control quartzware protocols are employed to ensure that the final products meet these specifications. Moreover, the quality control processes often involve instrumental analysis, such as mass spectrometry and infrared spectroscopy, to detect even trace levels of contaminants.
During the production of semiconductor grade quartz components, samples are frequently tested to ascertain their purity. This testing may include examining impurity levels across various wavelengths and utilizing sophisticated techniques to assess the structural integrity of the material. The goal is to eliminate any element that could potentially interfere with the semiconductor’s function. As semiconductor technology progresses, the need for increasingly pure materials intensifies, particularly for processes such as diffusion, where quartz tube for diffusion furnace applications plays a crucial role in achieving optimal results.
With the ever-evolving demands of the semiconductor industry, understanding and maintaining 99.99% SiO2 purity is crucial. It not only ensures high performance but also supports the long-term reliability of devices, demonstrating the integral role that quartz glass purity plays in modern electronics.
The Effects of Impurities on Semiconductor Performance
In the realm of semiconductor manufacturing, the purity of materials used is paramount. Quartz glass purity, particularly that of high purity fused quartz semiconductor, plays a crucial role in determining the overall efficacy and reliability of electronic components. Impurities, whether they stem from the environment, processing, or the quartz itself, can significantly influence the performance of semiconductor devices. Even minute levels of impurities can lead to substantial failures in the final products.
Common impurities found in quartz glass include metal ions, organic compounds, and other particulates. These contaminants can disrupt the electrical characteristics of semiconductor materials. For instance, metal ions like iron or aluminum can introduce charge carriers that alter the electrical conductivity of the silicon substrate. Consequently, devices fabricated with these contaminated materials may exhibit poor performance, high leakage currents, and reduced yield rates.
Moreover, the effects of impurities on wafer yield can be profound. When semiconductor grade quartz components contain even trace amounts of contaminants, the risk of defects during the fabrication process escalates. These defects can lead to an increase in defect density on the wafer, leading to lower manufacturing yields and potentially causing costly waste. In thus, thorough contamination control quartzware practices are essential. Employing quartz tubes for diffusion furnace applications that are designed for increased purity can greatly enhance the reliability of semiconductor manufacturing processes.
Studies have shown that impurities in quartz glass can lead to inconsistencies in doping concentrations during the fabrication phase, which also adversely affects device performance. The performance of capacitors, transistors, and other essential components in the semiconductor industry hinges on the use of quartz glass with an elevated purity level of 99.99% SiO2. Thus, ensuring that manufacturers remain vigilant regarding quartz glass purity can lead to more effective and reliable electronic components.
Manufacturing Processes for High-Purity Quartz Glass
High-purity quartz glass, particularly with 99.99% SiO2 content, is essential in semiconductor manufacturing due to its unique properties, such as thermal stability, low expansion coefficient, and outstanding optical clarity. The manufacturing processes employed to produce quartz glass must be meticulously controlled to achieve the required purity levels essential for semiconductor applications.
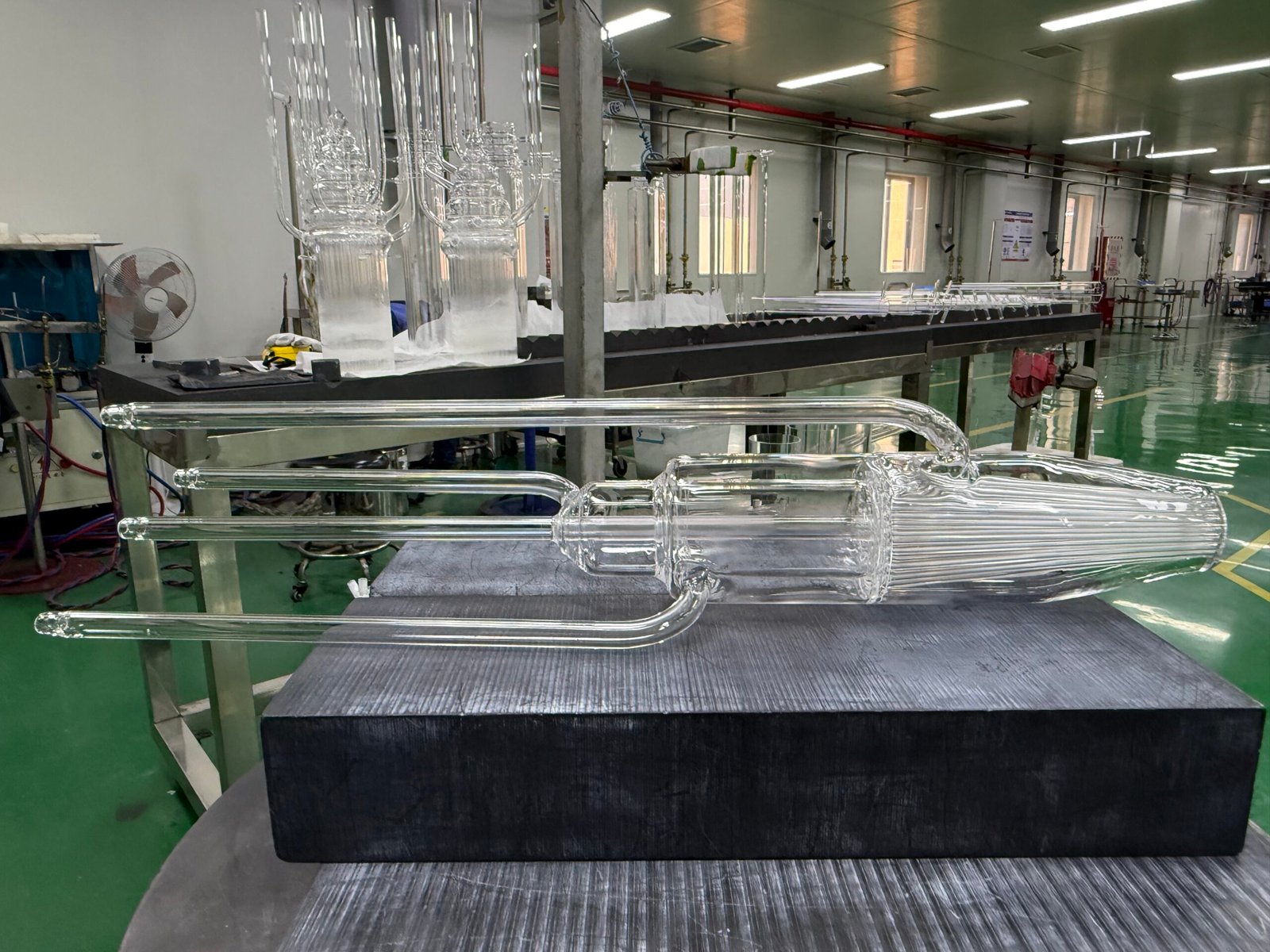
The first step in producing high-purity fused quartz involves refining naturally mined silica. This process is critical, as impurities found in raw silica can significantly impact the final product’s quality. During refining, the silica is treated to eliminate contaminants, including metal oxides and organic materials, ensuring that the quartz glass produced meets stringent standards for semiconductor-grade quartz components.
Once refined, the next step is melting. This occurs in a high-temperature environment using electric furnaces, which are designed for contamination control quartzware. In these furnaces, the refined silica is heated to its melting point, allowing any remaining impurities to be eliminated as gas. This stage is pivotal for attaining a low concentration of impurities, which could otherwise compromise the functionality of semiconductor devices. Furthermore, the melting process must be performed in a controlled atmosphere to prevent any potential contamination.
Following melting, the molten quartz is shaped and formed into desired geometries, such as tubes or plates, which are essential in various semiconductor manufacturing processes, including the use of quartz tubes for diffusion furnaces. Maintaining temperature and environmental parameters during the forming process is crucial, as it prevents the introduction of any additional contaminants that could affect the purity of the finished product.
Each manufacturing stage is interconnected and requires strict adherence to purity protocols. The effects of impurities on wafer yield are substantial, making it essential for manufacturers to ensure that every step optimally contributes to producing high-purity quartz glass. Properly executed, these processes yield semiconductor-grade quartz components that meet the rigorous demands of modern technology.
Comparison of Different Grades of Quartz Glass
Quartz glass is classified into various grades based on its purity level, with the most prominent being high purity fused quartz which contains 99.99% SiO2. This grade is integral in semiconductor manufacturing due to its minimal contamination levels and exceptional thermal stability. When compared to lower grades, such as commercial quartz glass which may contain impurities up to 1%, the advantages of utilizing high purity fused quartz become evident.
Lower grades of quartz glass, while applicable for certain industrial uses, are often not suitable for semiconductor applications. Their increased impurity levels can significantly affect the performance of semiconductor devices. Impurities in quartz glass can lead to adverse effects on wafer yield, which in turn impacts the overall efficiency and reliability of the semiconductor products produced. Such variations make understanding quartz glass purity essential for professionals in the semiconductor field.
In practical terms, the differences in purity levels affect the types of quartz components used in manufacturing processes. High purity fused quartz semiconductor components, for instance, are crucial when it comes to processes such as diffusion in quartz tubes for diffusion furnaces. Here, equipment must maintain strict contamination control quartzware to ensure optimal results. Any additional contaminants from lower-grade quartz may lead to defects, necessitating further investments in quality control and potentially leading to decreased production capabilities.
Thus, the choice of quartz glass grade is pivotal for manufacturers aiming for high-quality outcomes in semiconductor fabrication. The operational subtleties highlighted by the distinct grades illustrate that investment in 99.99% SiO2 materials is fundamental for enhancing device performance and overall yield. Furthermore, leveraging high purity materials aids in achieving the stringent contamination control standards necessary for successful semiconductor manufacturing.
Challenges in Achieving and Maintaining Purity
Achieving and maintaining quartz glass purity, particularly for high purity fused quartz semiconductor applications, presents several significant challenges. The quest for quartz glass composition that boasts 99.99% SiO2 is often complicated by potential contamination sources that can originate during production processes, storage, and transportation.
During the manufacturing process, even the smallest amount of impurities can compromise the quality and performance of quartz glass. Raw material selection is paramount; however, contaminants may be introduced through the handling of materials and the tools used in the production line. For instance, if the equipment is not properly cleaned or maintained, residual substances may lead to defects that directly affect semiconductor yield. It is imperative for manufacturers to implement stringent contamination control quartzware procedures to mitigate these risks and ensure the integrity of the high purity fused quartz semiconductor.
Storage and transportation are also critical stages where quartz glass purity can be compromised. Environmental factors such as dust, humidity, and temperature fluctuations can trigger contamination. Therefore, maintaining an appropriate storage environment is essential. This includes the use of specialized containers and storage facilities that are designed to limit exposure to these adverse conditions. Additionally, careful handling during transport is necessary to prevent abrasions or scratches on the quartz tubes, which can further lead to contamination that negatively impacts wafer yield.
To combat these challenges, the semiconductor industry has adopted numerous strategies. Advanced quality control systems are employed to routinely monitor the purity levels of quartz components throughout each phase. Furthermore, investing in customized packaging and transport solutions has proven effective in safeguarding high purity quartz glass from potential contaminants. Although maintaining quartz glass purity at 99.99% SiO2 may be complex, diligent efforts and state-of-the-art practices can greatly enhance the production of reliable semiconductor components.
Future Trends in Quartz Glass Purity and Semiconductor Manufacturing
The semiconductor industry is facing increasing demands for higher performance and efficiency, necessitating advancements in manufacturing materials and processes. A key component in this evolution is quartz glass purity, with a focus on achieving 99.99% SiO2 content. As the need for high purity fused quartz semiconductor components becomes critical, there is a noticeable trend towards the development of innovative purification techniques that enhance the quality of quartz glass. These techniques aim to reduce the presence of impurities which can adversely affect wafer yield, thereby potentially increasing production costs and affecting overall device performance.
One emerging technology involves improved contamination control quartzware, which utilizes advanced cleaning protocols and contamination prevention measures tailored for the rigorous environments of semiconductor manufacturing. Moreover, researchers are exploring novel deposition and synthesis methods that not only enhance the structural integrity and purity of quartz but also adapt to the specific requirements of semiconductor applications. This shift towards high purity materials is driven by the growing complexities of semiconductor devices and their manufacturing processes.
The use of quartz tubes for diffusion furnaces exemplifies the necessity for high purity levels. As device feature sizes shrink, even minute levels of contamination can lead to significant degradation in device performance. Advancements in the design and fabrication of these tubes are crucial for ensuring low contamination rates, thereby directly influencing production yield. Additionally, industry collaboration between material scientists and semiconductor manufacturers will further promote innovations aimed at refining quartz glass quality.
Looking ahead, it is evident that continued investment in research and development will play a pivotal role in shaping the future landscape of quartz glass purity and its applications in semiconductor manufacturing. By consistently pushing the boundaries of material science, the industry will be better equipped to meet the evolving demands of high-performance electronics.